To begin diagnosing your vision problems, a thorough medical and ocular history will be taken. Your vision will be checked, and then your eyes will be dilated with eye drops. These drops dilate the pupil so that the doctor can see to the back of the eye. Dilation typically lasts three to four hours. Initial consultation may take 3 hours in the office since most diagnostic testing and treatments can be offered on the same day. Follow up evaluations typically take much less time.
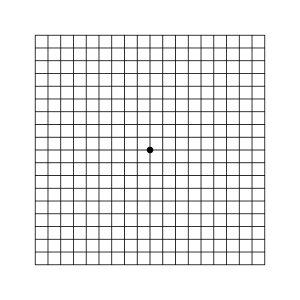
Amsler Grid Testing
Amsler grid testing is a very sensitive method of detecting early changes in your central vision. Detection of retinal diseases, such as macular degeneration, in its early stages may prevent serious loss of vision.
- Place the Amsler grid in a convenient place approximately 18 inches away, or normal reading distance.
- Check each eye separately while covering the other eye. If you wear glasses for reading, use them during this test.
- Look directly at the black dot in the center of the grid. Use your side vision to see the other lines of the grid without moving your focus from the center dot.
- Note any irregularities of the grid patter such as bent, fuzzy, or wavy lines or dark or missing spots. Draw these on the printed grid and date them.
If you notice a change in your vision on the Amsler grid test, you should contact us. Particular attention should be given to sudden changes.
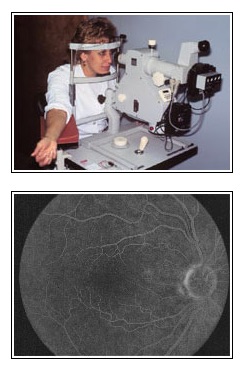
Angiography
Fluorescein Angiography
This test is very useful in evaluating problems of the macula, or the center of the retina. A vegetable-based dye is injected into the arm and then photographs are taken of the back of the eye as the dye circulates throughout the body and the blood vessels in the retina.
Many diseases of the macula will be seen as to “light up” as it passes through the blood vessels of the eye allowing for timely management. Thanks to a completely computerized camera and screen, results can be seen immediately and can be stored for future comparison.
Indocyanine Green (ICG) Angiography
This test is similar to fluorescein angiography in that a dye is injected into the vein in the arm and we take photographs over time to help us diagnose problems in the back of the eye. The difference, however, is that the dye is used to study mainly the choroidal circulation, or the layer of blood vessels underneath the retina. ICG angiography is used less frequently than fluorescein angiography, but it can be especially useful in cases where blood obscures visualization of the retina. ICG angiography is also performed with a digital (computerized) system at Retina Care Specialists, allowing for immediate interpretation by the physician.
Fundus Photography
Specialized cameras for the back of the eye can be used to monitor eye problems such as diabetic retinopathy or other findings in the back of the eye. This way, the doctor can make an accurate comparison when you come back for a follow-up visit.
Optical Coherence Tomography
This test is used to produce detailed images of the retina. It is much like ultrasound, except that it uses light beams instead of sound waves. Optical Coherence Tomography helps physicians evaluate problems with the retina such as swelling and holes, as well as abnormalities of the optic nerve.
During the exam, focused beams of light are directed into the eye. The light beams scan the structural features of the retina, producing
a cross-section image similar to a topographical map. The test takes about 3 to 5 minutes and usually requires dilation of the pupils.
Ophthalmoscopy

Ophthalmoscopy is the detailed and complete visual examination of the retina and vitreous by the ophthalmologist. We use a slit-lamp biomicroscope, where a focused beam of light is used to evauate the macula with magnification. Indirect ophthalmoscopy is where a hand-held lens is used to direct light from a headlight worn by the doctor. The light is directed onto the retina and allows the doctor to see a panoramic view of the entire retina, including the retinal periphery.
Ultrasonography
This is a non-invasive test involving a specialized sonogram probe, and it is used when a cloudy cataract, cornea, or blood in the middle of the eye prevents a good view of the retina. It is also useful in evaluating the extent and nature of retinal detachments, and in following the size of lesions in the eye such as choroidal nevi. The B-scan ultrasound creates a two-dimensional image. A scan creates a one-dimensional view, which in retinal care, is usually used to determine the density of a given structure.
Visual Acuity Testing
This is a simple but important part of the eye exam. Here the ability to identify letters at a specified distance is tested. It is best to wear your most recent glasses or contact lenses if applicable for this test.